The concept of traceability within the dairy supply chain is integral to the modern agricultural paradigm, crucially supporting food safety and quality management systems. Traceability pertains to the systematic ability to track and document the production, movement, and history of dairy products from their source—be it a dairy farm or grazing field—through the stages of processing and distribution until they are delivered to the consumer. This comprehensive tracking is essential for verifying the provenance of dairy commodities, managing recalls efficiently, and ultimately ensuring the integrity of the product.
Furthermore, as dairy products transition from farm to plate, every transaction and transformation, ranging from feeding and milking of animals, storage and transportation of raw milk, pasteurization, and packaging, to the final sale, must be clearly recorded and accessible. Advanced technologies such as RFID tagging, GPS tracking, and blockchain ledger systems are increasingly employed to offer real-time monitoring and immutable records.
Establishing such traceability frameworks sets a stage that not only elevates consumer trust but also enables producers and regulatory bodies to swiftly react to and contain any issues related to foodborne illnesses, thereby securing the health of the end consumer and the longevity of the dairy industry.
From Meadow to Mug: The Rocky Route of the Dairy Supply Chain
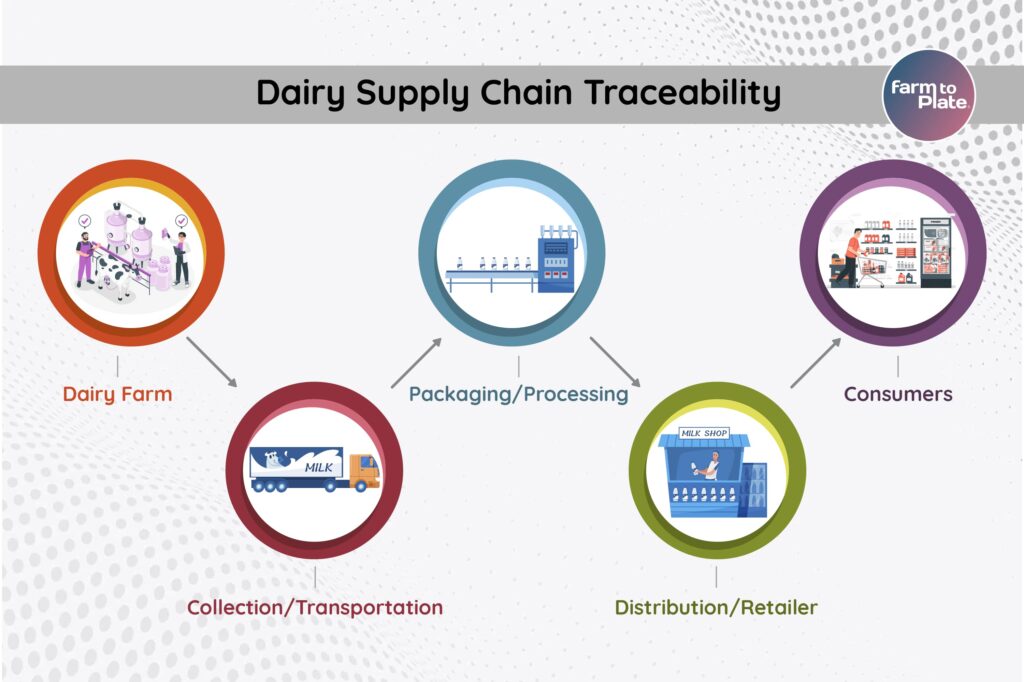
The journey of dairy from a lush meadow to a steaming mug is a complex one, woven with numerous critical steps. Each stage of this supply chain is vital and carries with it the responsibility of maintaining the integrity, quality, and sustainability of the end product. Let’s delve into each stage and explore the benefits of implementing Farm To Plate (F2P) strategies and what can be traced throughout the process.
From the milkman to the final product, every detail counts. Here’s how our latest digital capture technology is revolutionizing the process:
Dairy Farm:
To commence traceability, the process begins by capturing the milkman’s name. Recording the details of milk collection enhances efficiency and aids in demand forecasting. Every lot collected is quantified and assigned a unique number, facilitating precise inventory management and batch tracking. Both the timestamp and location of each lot are documented to ensure accountability. These records will be reinforced with visual documentation—photographs and videos—providing a verifiable account of the milk’s origin. Furthermore, technologically advanced methods are utilized to capture data on raw ingredients even in remote locations with limited network connectivity.
Collection/Transportation:
To ensure the integrity of our produce from catch to delivery, each catch is meticulously recorded with the date, time, and corroborating visual evidence—photos and videos. The catch’s live geographic location is instantly shared. Upon arrival, each batch undergoes stringent quality control checks to confirm its quality. The produce is then packaged as per client requirements, catering to processors, manufacturers, or distributors.
QR codes are applied for enhanced traceability and lot history. Shipments are labeled with the processor organization’s identity and monitored with real-time tracking to confirm successful delivery. Throughout transit, IoT technology is employed to continuously record temperature and humidity, preserving the quality of the shipment. Instant app notifications alert us to any unexpected stops, while detailed analytics provide insights into any shrinkage or theft during the product’s journey.
Packaging/Processing:
All goods received are promptly logged, with shrinkage closely monitored and the entire journey of product transformation meticulously documented from the raw state to finished goods. New food batches are produced and facilitate traceability by assigning system-generated QR codes to designate quantities to specific lots, which are also clearly labeled for efficient tracking.
Every product’s shelf life is recorded, inventory is diligently managed by location, and we enable real-time tracking of shipment locations until the point of delivery. Utilizing IoT sensors, transit conditions, such as temperature and humidity, are continuously measured, ensuring product quality and maintaining vigilance with in-app alerts that notify us of any transit stoppages or incidents of shrinkage or pilferage.
Distribution/Retailer:
Upon the reception of goods, it is crucial to meticulously record the arrival and evaluate for any potential shrinkage, while simultaneously accessing the wealth of product details and logistics data, such as shipment specifics, and tracking the transportation vehicles involved. The emphasis on maintaining product integrity is non-negotiable; this is achieved through diligent contamination checks, assigning separate lots tailored to each order, and preparing the packaging accordingly for retailer shipment.
Warehouse operations are amplified with cutting-edge technology; real-time monitoring of shipments is now standard, coupled with precise management of inventory that varies by location, ensuring deliveries are on track every step of the way. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors provides another layer of oversight, offering temperature and humidity monitoring during transit. These capabilities empower businesses with proactive in-app notifications for any interruptions and access to thorough reports on shrinkage or theft, ensuring a transparent and secure supply chain from start to finish.
Consumers:
In retail stores, each item’s QR code serves as a gateway to its provenance. A quick scan allows customers to view a comprehensive product journey, including information about its source and shelf life, right at their fingertips. Beyond mere tracking, the platform extends to interactions such as tipping the milkman for their delivery service directly through the system. Customers can also actively participate by rating the ingredients, thus providing valuable feedback. This level of transparent communication available on the journey detail page not only enlightens consumers but also cultivates a deeper level of trust with the product owner, ushering in a new era of informed purchasing.
Technology and Traceability in the Dairy Supply Chain

In recent years, the dairy industry has seen significant advancements in technology, especially in the areas of traceability and transparency. These developments are not only improving efficiency and productivity but also enhancing the accountability and ethical standards of the supply chain. Let’s delve into some of these technological breakthroughs.
1. Tracking Systems
One of the core components of modern supply chains is a sophisticated tracking system. These systems enable companies to monitor the movement of dairy products from farm to factory to consumer. They often utilize complex software that can record and manage data across the entire supply chain.
- Barcoding and QR codes: Simple yet powerful, these methods allow for easy scanning and information retrieval at any point in the supply chain.
- Database Technologies: Centralized databases can store vast amounts of information that is instantly accessible to stakeholders, such as production dates, batch numbers, and shipment details.
2. RFID Technology
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been a game-changer for traceability in the dairy supply chain.
- Tagging Livestock: RFID tags can be used to track the health, production, and movement of individual animals, providing a detailed history of the milk’s origin.
- Automated Data Capture: By automating data capture, RFID reduces the risk of human error and increases the accuracy of the records.
3. Sensors and IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled the integration of sensors throughout the dairy supply chain, which can monitor conditions in real-time.
- Temperature Monitoring: Crucial for maintaining the quality of dairy products, sensors can detect temperature deviations that may spoil the product.
- Fleet Tracking: GPS technology and IoT devices enable real-time tracking of delivery vehicles, ensuring timely and efficient distribution.
4. Blockchain for Dairy
Blockchain technology proponents suggest it can add a new level of security and transparency to traceability systems.
- Immutable Records: Once a piece of information is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be altered, increasing the confidence in the data provided.
- Decentralization: The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that the data is not controlled by a single entity, which can help prevent fraud.
5. Sustainable Farming Practices
The role of the dairy farm in ensuring quality cannot be overstated, and technology is playing a big part in promoting sustainable practices.
- Precision Farming: The use of technology to precisely manage resources, such as water and feed, optimizes production and minimizes waste.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels and methane digesters can turn a dairy farm into a source of renewable energy, reducing its carbon footprint.
6. Ethical Production and Quality
The introduction of these technologies in the dairy farm sphere also plays a significant role in ensuring ethical production practices.
- Animal Welfare: Technology enables farmers to monitor animal health and welfare closely, ensuring humane treatment and quality of life for livestock.
- Quality Assurance: By tracking every step of the production and supply process, technology ensures that the final products meet high quality and safety standards.
Challenges in the Supply Chain of the Dairy Industry
- Agricultural Beginnings Dairy production begins with the farmers, who face impediments like disease in cows and varying environmental conditions that, directly affect milk’s volume and integrity.
- Processing Precision Post-milking, the focus shifts to processing facilities that prioritize cleanliness, operational efficacy, and adhering to diverse food safety norms to ensure milk is uncontaminated and up to standards.
- Distribution Dynamics The perishable nature of dairy necessitates an unbroken and well-regulated cold chain to keep the products fresh. Logistics must be seamless to align with consumer demands and circumvent spoilage.
- Retail Responsiveness Dairy products reach retail shelves, where inventory control is key. Staff training on product care ensures the longest possible shelf life and the provision of high-quality goods.
- Strategic Implementation Ingraining these considerations within the dairy industry’s framework can foster advanced methods to tackle these issues, enhancing overall performance and resilience. All members, from producers to end consumers, stand to gain when strategies are implemented for a more efficient journey from farm to table. Let’s delve into the methodologies and breakthroughs leading to a streamlined dairy path.
Quality Assurance and Testing in the Dairy Product Supply Chain
Quality assurance in the dairy product supply chain is critical to ensuring that every product reaching the consumer is fresh, safe, and in compliance with relevant regulations. The process starts at the dairy farms, where milk is produced, and extends all the way to the table of the consumer. Here are the typical measures in place throughout the supply chain:
- At the Farm
- Regular Health Checks: Dairy animals are regularly examined to maintain a healthy herd.
- Clean Milking Practices: Ensuring the milking equipment and environment are clean is crucial to preventing contamination.
- Milk Sampling: Immediate testing of milk for antibiotics and somatic cell counts to ensure milk quality.
- During Processing
- Pasteurization: Virtually all milk is pasteurized to eliminate harmful pathogens.
- Batch Testing: Regular testing for consistency, flavor, and bacterial content.
- Packaging Controls: To prevent contamination during the packaging process.
- In Transit
- Cold Chain Management: Continuous refrigeration to maintain freshness during transportation.
- Periodic Sampling: Testing for temperature abuse and other quality parameters.
- At Retail
- Shelf-life Monitoring: Ensuring products are sold before the expiration date.
- Store Handling Audits: Regular checks to confirm proper handling and storage by retailers.
Regular testing for freshness, safety, and compliance ensures that any issues can be identified and addressed quickly, often before products reach the consumer. This proactive approach to quality control significantly contributes to consumer confidence, knowing that the dairy products they consume are of the highest standard.
Farm To Plate: Enhancing Dairy Industry Traceability Through Blockchain
Farm To Plate (F2P) leverages blockchain technology to revolutionize traceability in the dairy industry. This system offers enhanced traceability, providing all participants in the supply chain—from farmers to retailers—real-time data on the movement of dairy products. This ensures a transparent history of the products, including details of farm conditions, processing, transportation, and retail handling.
In terms of safety, blockchain’s rapid traceability facilitates swift action in the case of contamination, allowing authorities to quickly pinpoint the source. Consequently, this leads to more targeted recalls, thereby minimizing waste and ensuring consumer protection.
Wrapping UP
Traceability is pivotal for the credibility of the dairy supply chain, connecting producers to consumers with trust and transparency. Farm To Plate (F2P) effectively addresses the demands of traceability, ensuring accountability and product integrity. Acknowledging this journey from farm to plate highlights the role traceability plays in securing the excellence of the dairy products we rely on.
FAQ’s
How is blockchain used in the dairy industry?
Blockchain is utilized to create an unchangeable ledger of all transactions and movements within the dairy industry, from the farm, during processing, through distribution, and to the retail store.
What is the milk supply chain strategy?
The milk supply chain strategy involves the planning and management of milk production, collection, processing, distribution, and retail to ensure efficiency, sustainability, and product quality consistency.
Why is the milk supply chain important?
The milk supply chain is essential to ensuring that fresh, high-quality milk and dairy products are delivered to the consumer efficiently and sustainably while meeting safety and regulatory standards.
What is traceability in the dairy industry?
Traceability in the dairy industry refers to the ability to track every step of the dairy product’s journey from the farm where it was produced, through processing and distribution, to the final consumer. This is essential for safety, quality assurance, and meeting legal requirements.
Sravya Priya, Content Marketing Specialist at farmtoplate.io
